Mirage M-2000C
| This is a beta module.
This module is still being developed and may still be missing some features and equipment options. It is playable and most of the content is there, but some final touches and fixes for minor bugs are still in the works. It is probably safe to buy unless you crave absolute fidelity and/or very few bugs. |
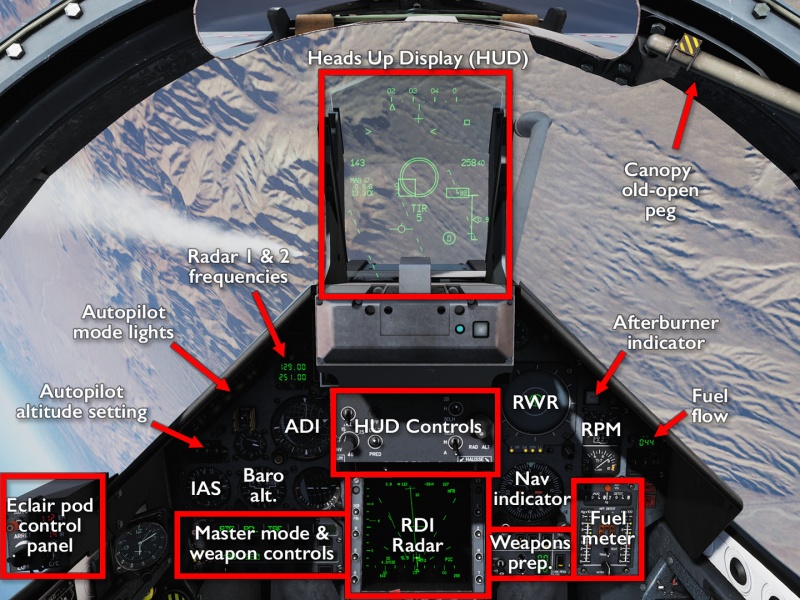
The Dassault Mirage 2000C is a supersonic multirole fly-by-wire delta-wing aircraft, which sans technobabble means it is fast and nimble and capable of both air-to-air and air-to-ground combat. Of the two tasks, the C model (for “Chasseur,” or fighter) is more at home in the air-to-air role, featuring DCS's first proper BVR radar to be featured in any of the full-fidelity, non-FC3 aircraft. Before this, there were only the F-5E-3, that had no radar-guided weapons, and the MiG-21bis that had no look-down capabilities, neither of which offered any kind of tracking or target information — only an indistinct blip to steer towards.
Some would argue that the M-2000C's radar, with its need to pick the right filtering modes and scan zones and antenna elevation and, consequently, with its tendency to lose track of a target at the most inopportune moments, is no better than those earlier modules. Those people are silly and wrong.
Features
The M-2000C's air-to-air focus is made further evident by its features list:
- A Mach 2+ top speed and ridiculous climb rate.
- Matra Magic IR missiles and Super-530D semi-active radar homing missiles.
- A built-in ECM pod and countermeasure pods that contain tons of chaff, but very few flares, and a competent RWR to help with employing them properly.
- The option to replace its very handy landing drag chute with an additional “Eclair” countermeasure pod to augment and balance the two out a bit.
- Limited and inaccurate CCIP and CCRP modes that are tied to specific bombs rather than selectable by the pilot.
- In spite of that, the ability to carry a respectable number of bombs, including LGBs.
To get to where it needs to go, the M-2000C also features:
- A complex but very competent inertial navigation system.
- TACAN navigation, with a built-in special mode to navigate to TACAN offset point.
- Thanks to its FBW control system, a very competent and flexible autopilot, including an ILS-guided auto-landing mode.
In many ways, then, the M-2000C is very much like a more fully-developed and advanced version of the F-5E-3 — if you like flying the MiG-28 Tiger, chances are that you will enjoy flying the Baguette as well.
Comes with the built-in M-2000C Campaign.
Missing features
The M-2000C is for the most part a finished product — finished enough, at least, to not be marked as “early access” in the DCS shop. It earns its “beta” status mainly due to a number of missing (supposedly upcoming) features to the VTB/HDD radar display:
- Most target information switches are not functioning.
- Ground mapping radar is missing.
- GCI navigation mode is missing (but unlikely to ever be implemented).
- Proper CCRP and consent-to-release functionality.
Flying the M-2000C
The M-2000C is very very easy to fly thanks to its fly-by-wire controls. You point the flight path marker where you want to go and the computers try go get you there. If they can not, they keep trying until you have no energy and fall belly-first into the ground. Departure from controlled flight invariably manifests itself as the airplane pointing in one direction, but gently and inevitably sliding off in another, and getting out of it is mostly about convincing the computer that, no, you actually want to try a more fruitful direction that the one it is currently struggling to maintain. Almost always, this means forcing the aircraft into the ground and ignoring the screaming warnings, possibly in combination with some deliberate pilot-induced oscillation to forcibly overload the FBW system.
Under more normal flight conditions, it gets even easier since the FBW enables and drives an advanced, but very simple to use, autopilot system. In its most basic mode, it simply holds the current attitude and that attitude can be adjusted by moving a steering dot around on the HUD with the trim hat.Alternatively, you can momentarily pause the AP with a button press, manually the aircraft, and the AP will hold whatever attitude it is in when the button is released. In the more advanced altitude hold modes (yes, plural) it either holds the current altitude or holds a set altitude once reached. Here, the trim hat changes the altitude and also dials in a course heading on the nav indicator. Finally, there is the approach mode, that follows a captured ILS signal down to the threshold — under good conditions, it takes the plane all the way down to the tarmac (but do not rely on it — hands on stick at all times). Note that none of these modes (especially not the landing AP) automate the throttle. It is up to the pilot to maintain proper thrust at all times.
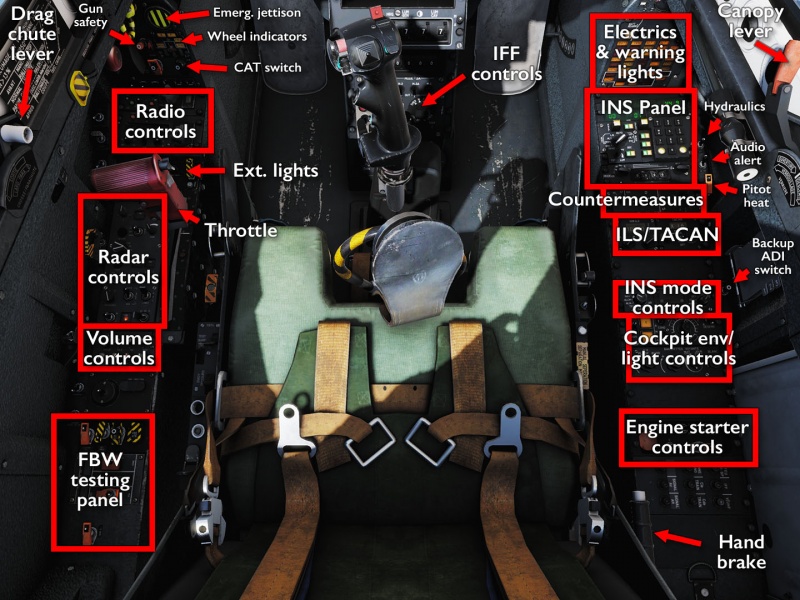
Cockpit overview
Getting into the air
Getting the M-2000C started is, on the one hand, very easy: just flip everything on — preferably, but not necessarily, in the right order — and the difficulty lies in remembering every little nook and cranny that there are switches in. On the other hand, it is a very long-winded process, due to two of the more complicated on-board systems: the INS and the FBW.
The inertial navigation system needs to be initialised, aligned, and possibly even programmed with waypoints if the mission itself does not provide them. The alignment is a five-minute process; the waypoint input can take a very long time if it is a complicated route or if lots of details are added to it. You can certainly take off without the INS working, but of course, you will be relying on visual or radio navigation at that point.
Similarly, the fly-by-wire system and autopilot require a fair amount of testing to give a green light and be safe for operation. It is also a bit annoying because, while completely automated, it is just long enough that it is not just something you speed by, but at the same time, it is just short enough that it does not really give you any good opportunity to deal with some other system setup at the same time. Again, you can take off without these tests, but a very angry red warning light will be glaring at you throughout the entire flight, and if something goes wrong, you might not know it.
For those in a hurry, the aircraft has the fairly standardised RWinHome “cheat” hotkey to run through the startup process. For everyone else, the procedure consists of:
- Turn on battery, tansformer, and alternators.
- Check your kneeboard(!) — it contains the information you need for alignment and is also used to set up some weapons (notably LGBs) that cannot be adjusted on the fly once you are off the ground.
- Start INS alignment. While it is going, check that the waypoints are set up and/or input them yourself while yelling at the ground crew/mission designer.
- Make sure the hand brake is on.
- Turn on fuel pumps, air vents, and press the start button.
- Push the throttle just out of idle to get it going, then make sure it settles within proper working parameters.
- Turn on everything else that you'll need (in particular, start pre-heating the radar).
- Test the FBW system.
- By now, the INS should be aligned — turn it on properly.
- Set up what's left (CAT, radar modes, radios, countermeasures etc).
- Remember that you have a handbrake and disengage it before rolling out.
The full process, and in particular the differing methods for aligning the INS, are described in more detail in the manual, and in the checklist and, as usual, Chuck's guide linked below.
Shooting something
Smart weapons
Links and files
- Tippis' Checklist (see also kneeboard mods).
- Chuck's M-2000C guide.
- DCS: M-2000C by RAZBAM in the DCS shop.
Related DCS modules
- 'M-2000C Red Flag Campaign by Baltic Dragon'
More information
- Dassault Mirage 2000 on wikpedia.
- Mirage 2000 (Dassault-Breguet) on globalsecurity.org
- Bunyap's Test Flight - DCS: Mirage 2000C video series.